The Pittsburgh Cycle, also known as the American Century Cycle, is August Wilson’s magnum opus, a series of ten plays that charts the African American experience throughout the twentieth century. “Put them all together,” Wilson once said, “and you have a history.” All of the plays are set in Pittsburgh’s Hill District except for Ma Rainey’s Black Bottom, which is set in Chicago.
Wilson didn’t actually plan to write a 10-play cycle. “I didn’t start out with a grand idea. I wrote a play called Jitney set in ’77 and a[n unpublished and unperformed] play called Fullerton Street that I set in ’41,” he told author and teacher Sandra Shannon. “Then I wrote Ma Rainey’s Black Bottom, which I set in ’27, and it was after I did that I said, ‘I’ve written three plays in three different decades, so why don’t I just continue doing that?’” (Fassler)
Characters in the plays often appear at different stages of their lives, with the offspring of previous characters cropping up in later plays. The figure of Aunt Ester features most often in the cycle. Other recurring elements include the use of music and the presence of an apparently mentally-impaired character; examples include Gabriel in Fences and Hedley in Seven Guitars.
Gem of the Ocean
Nominee, Tony Award, 2005
Gem of the Ocean is set in 1904 in the Pittsburgh home of Aunt Ester, a 285-year-old former slave and renowned cleanser of souls. A young man from Alabama visits her for help in absolving the guilt and shame he carries from a crime he’s committed, and she takes him on a journey of self-discovery to the City of Bones.
Joe Turner’s Come and Gone
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Nominee, Tony Award, 1988
Set in a Pittsburgh boardinghouse, Joe Turner’s Come and Gone tells the story of owners Seth and Bertha Holly and the makeshift family of migrants who pass through during the Great Migration of the 1910s.

Joe Turner’s Come and Gone at Yale Repertory Theatre. William B. Carter, 1986. Courtesy of Yale Repertory Theatre.
Ma Rainey’s Black Bottom
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Nominee, Tony Award, 1985
Set in 1927. Legendary blues singer Ma Rainey and her band players convene in a Chicago studio to record a new album. As their conversation unfolds, their bantering, storytelling and arguing raise questions of race, art and the historic exploitation of black recording artists by white producers. Ma Rainey’s Black Bottom is being released by Netflix in December, starring Viola Davis as Ma Rainey and Chadwick Boseman, in his last performance, as the young jazz musician Levee.
The Piano Lesson
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Pulitzer Prize for Drama, 1990
Nominee, Tony Award, 1990
The Piano Lesson is set in 1936 Pittsburgh during the aftermath of the Great Depression. The play deals with themes of family legacy. Brother and sister Boy Willie and Berniece Charles clash over whether or not they should sell an ancient piano that was exchanged for their great-grandfather’s wife and son in the days of slavery. The Piano Lesson was made into a Hallmark Hall of Fame movie in 1995, the first of Wilson’s plays to be filmed for a large audience.
Seven Guitars
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Nominee, Pulitzer Prize for Drama, 1995
Nominee, Tony Award, 1996
A blues singer just released from prison is asked to sign a record deal after a song he recorded months before becomes an unexpected hit in 1948. He is ready to right the past year’s wrongs and return to Chicago with a new understanding of what’s important in his life. Unfortunately his means of righting wrongs are inherently flawed.

A 2018 production of Seven Guitars by Miami’s M Ensemble Theatre
Fences
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Pulitzer Prize for Drama, 1987
Winner, Tony Award, 1987
Set in 1950s Pittsburgh, Fences tells the story of Troy Maxson, a restless trash-collector and former baseball athlete. Troy has gone through life in an America where to be proud and black is to face pressures that could crush a man, body and soul. But the 1950s are yielding to the new spirit of liberation in the 1960s, a spirit that is changing the world Troy has learned to deal with the only way he can, a spirit that is making him a stranger, angry and afraid, in a world he never knew and to a wife and son he understands less and less.
 Mary Alice, James Earl Jones and Courtney Vance in Fences at Yale Repertory Theatre. William B. Carter, 1985. Courtesy of Yale Repertory Theatre
Mary Alice, James Earl Jones and Courtney Vance in Fences at Yale Repertory Theatre. William B. Carter, 1985. Courtesy of Yale Repertory Theatre
Two Trains Running
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Nominee, Pulitzer Prize for Drama, 1992
Nominee, Tony Award, 1992
Two Trains Running is set in 1969. It tells the story of a local diner owner who fights to stay open as a municipal project encroaches on his establishment. His regulars must deal with racial inequality and the turbulent, changing times of the Civil Rights movement.
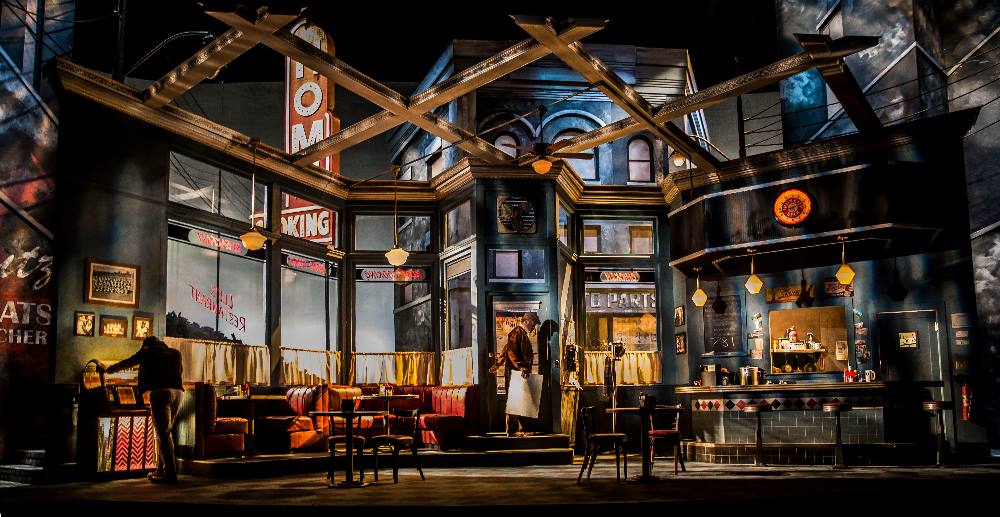 Production of Two Trains Running at the Goodman Theatre in Chicago.
Production of Two Trains Running at the Goodman Theatre in Chicago.
Jitney
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Set in 1977 in a worn-down gypsy cab station, Jitney tells the story of men hustling to make a living driving jitneys — unofficial and unlicensed taxi cabs — because official cabs will not accept jobs in the Hill District, and what the company and its drivers must consider when the building housing the station is slated for destruction. Jitney is the only one of Wilson’s plays not to have been produced on Broadway during Wilson’s life, although it had been performed off-Broadway and overseas. It finally made its Broadway debut in 2017.

Jitney at True Colors Theatre, Atlanta 2010
King Hedley II
Nominee, Pulitzer Prize for Drama, 2000
Nominee, Tony Award, 2001
One of Wilson’s darkest plays, King Hedley II tells the story of an ex-convict trying to rebuild his life by selling stolen refrigerators so that he can save enough money to buy a video store during the trickle-down economic era of the 1980s and a decaying Hill District. Many of the characters have connections to the characters in Wilson’s 1940s-era play Seven Guitars, showing “how the shadows of the past can reach into the present.” (Samuel French playscript Overview)
Radio Golf
Best Play, New York Drama Critics Circle
Radio Golf is set in 1997 in Pittsburgh’s Hill District. Aunt Ester returns in this story of a charming, powerful African-American politician who is running for the highest office of his career with the support of his savvy wife. As he steps into political prominence, his plans to redevelop the Hill District collide with his past.
Sources
https://augustwilsonblog.wordpress.com/tag/the-greene-space
http://www.august-wilson-theatre.com/plays.php
https://www.thegreenespace.org/watch/11-things-you-should-know-about-august-wilson
https://ronfassler.medium.com/the-magic-of-august-wilson-d6da37dbcfec


 Young August Kittel went to parochial school near his Hill District home on Bedford Avenue until his parents’ divorce. He, his mother, and his siblings moved from their historically black community to the Oakland neighborhood, which was primarily white. The constant bigotry of classmates led him to change high schools three times by the time he was fifteen, when he withdrew from formal school and began educating himself independently at Pittsburgh’s famed Carnegie Library. In 1962, at age 17, he enlisted in the Army but left after a year of service. After his father’s death in 1965, he took the name August Wilson to honor his mother.
Young August Kittel went to parochial school near his Hill District home on Bedford Avenue until his parents’ divorce. He, his mother, and his siblings moved from their historically black community to the Oakland neighborhood, which was primarily white. The constant bigotry of classmates led him to change high schools three times by the time he was fifteen, when he withdrew from formal school and began educating himself independently at Pittsburgh’s famed Carnegie Library. In 1962, at age 17, he enlisted in the Army but left after a year of service. After his father’s death in 1965, he took the name August Wilson to honor his mother. Pittsburgh’s Carnegie Library c. 1935
Pittsburgh’s Carnegie Library c. 1935 , was selected in 1982. Through the Conference, Wilson was introduced to the artistic director of the Yale Repertory Theatre, Lloyd Richards, who nurtured trailblazing playwright Lorraine Hansberry, the author of A Raisin in the Sun and the first African-American to have a play produced on Broadway. Richards helped shepherd the development of Ma Rainey’s Black Bottom and ended up directing Wilson’s first six plays on Broadway, including the 1987 Pulitzer Prize-winning Fences. Wilson earned his second Pulitzer in 1990 for The Piano Lesson.
, was selected in 1982. Through the Conference, Wilson was introduced to the artistic director of the Yale Repertory Theatre, Lloyd Richards, who nurtured trailblazing playwright Lorraine Hansberry, the author of A Raisin in the Sun and the first African-American to have a play produced on Broadway. Richards helped shepherd the development of Ma Rainey’s Black Bottom and ended up directing Wilson’s first six plays on Broadway, including the 1987 Pulitzer Prize-winning Fences. Wilson earned his second Pulitzer in 1990 for The Piano Lesson.
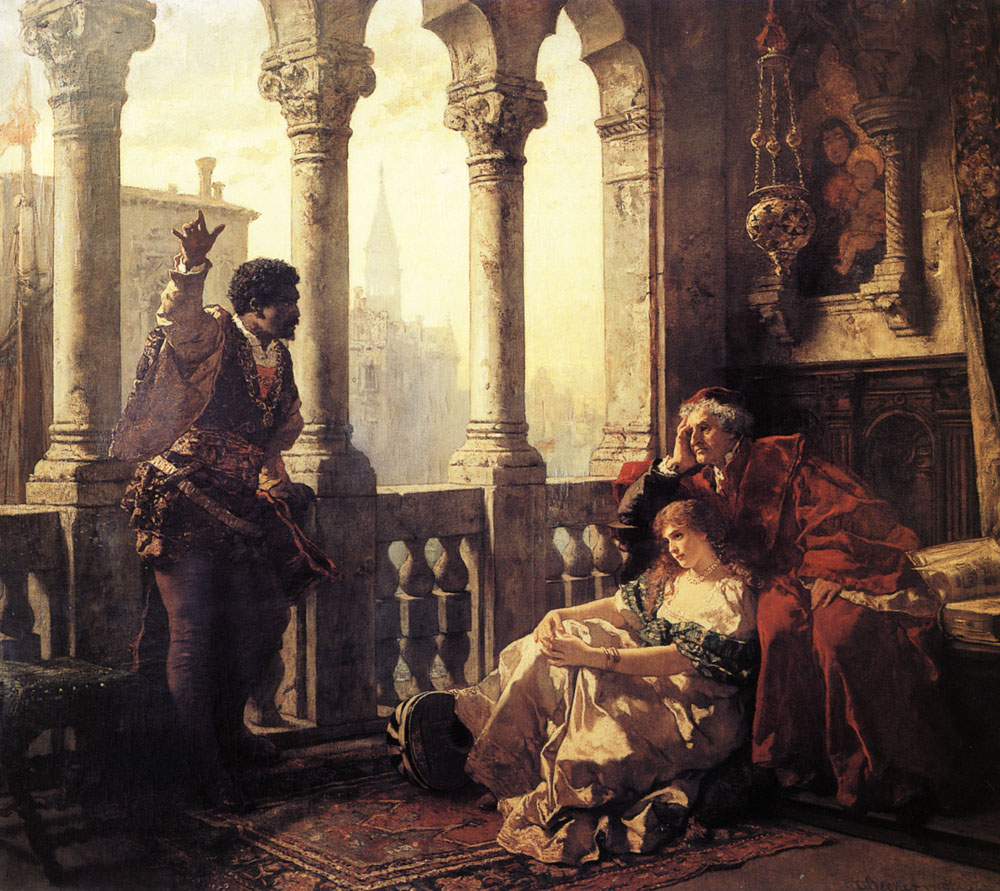



 Perhaps the best-known Othello in the United States is the renowned actor Paul Robeson. The son of an escaped slave, Robeson had built an international reputation not only from his role in the musical Show Boat, but as an athlete and an attorney. Robeson had a commanding physical presence that suited the role perfectly, but his casting against the young British actress Peggy Ashcroft in 1930 was not without controversy. Technical issues like poor staging and difficult acoustics made performing difficult. But no one argued with the power of Robeson’s performance. Ivor Brown, the critic for The Observer, described Robeson as “… an oak…a superb giant of the woods for the great hurricane of tragedy to whisper through, then rage upon, then break.” Audiences at the premiere gave Robeson twenty curtain calls. But, given the societal segregation of the time, Robeson had detractors as well who criticized everything from his interpretation of the role to how he pronounced the words of Shakespeare’s text. Samantha Ellis writes:
Perhaps the best-known Othello in the United States is the renowned actor Paul Robeson. The son of an escaped slave, Robeson had built an international reputation not only from his role in the musical Show Boat, but as an athlete and an attorney. Robeson had a commanding physical presence that suited the role perfectly, but his casting against the young British actress Peggy Ashcroft in 1930 was not without controversy. Technical issues like poor staging and difficult acoustics made performing difficult. But no one argued with the power of Robeson’s performance. Ivor Brown, the critic for The Observer, described Robeson as “… an oak…a superb giant of the woods for the great hurricane of tragedy to whisper through, then rage upon, then break.” Audiences at the premiere gave Robeson twenty curtain calls. But, given the societal segregation of the time, Robeson had detractors as well who criticized everything from his interpretation of the role to how he pronounced the words of Shakespeare’s text. Samantha Ellis writes: Despite the positive reception of an African-American actor in the role, the Oscar-nominated 1965 production (the highest number for a Shakespeare film in history) starring Sir Laurence Olivier and a very young Dame Maggie Smith as Desdemona reverted to type: The famous English actor played the role in makeup. This was the first cinematic Othello to be shot using color film, and Oliver was as meticulous about that as he was about developing the physical character through a deep voice and a special walk. He stated in an interview with Life magazine in 1964 that, “
Despite the positive reception of an African-American actor in the role, the Oscar-nominated 1965 production (the highest number for a Shakespeare film in history) starring Sir Laurence Olivier and a very young Dame Maggie Smith as Desdemona reverted to type: The famous English actor played the role in makeup. This was the first cinematic Othello to be shot using color film, and Oliver was as meticulous about that as he was about developing the physical character through a deep voice and a special walk. He stated in an interview with Life magazine in 1964 that, “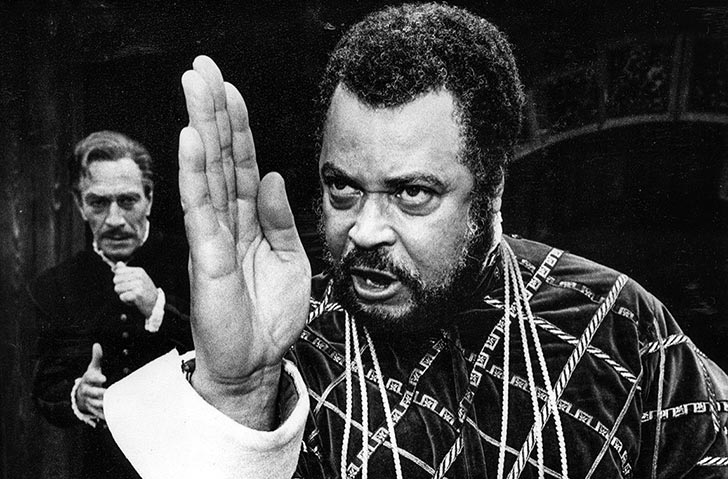 Perhaps the pushback against the Olivier production opened the door for the now generally-accepted casting of an African-American actor in the role. Famous Othellos of the last several decades include theater luminaries like James Earl Jones, Oscar-nominated actor Laurence Fishburne in a stellar 1995 production starring Kenneth Branagh as Iago and French actress Irene Jacob as Desdemona, and young actor Mekhi Phifer in “O,” a contemporary version that transforms the military conflict into a basketball rivalry set in a high school. Other famous actors who have played Othello include Orson Welles, Sir Anthony Hopkins, Chiwetel Ejiofor, and Eamonn Walker in a 2001 TV movie co-starring Christopher Eccleston (best known as the ninth Doctor Who) as Iago, which transplants the action from Venice and Cyprus to a London police station.
Perhaps the pushback against the Olivier production opened the door for the now generally-accepted casting of an African-American actor in the role. Famous Othellos of the last several decades include theater luminaries like James Earl Jones, Oscar-nominated actor Laurence Fishburne in a stellar 1995 production starring Kenneth Branagh as Iago and French actress Irene Jacob as Desdemona, and young actor Mekhi Phifer in “O,” a contemporary version that transforms the military conflict into a basketball rivalry set in a high school. Other famous actors who have played Othello include Orson Welles, Sir Anthony Hopkins, Chiwetel Ejiofor, and Eamonn Walker in a 2001 TV movie co-starring Christopher Eccleston (best known as the ninth Doctor Who) as Iago, which transplants the action from Venice and Cyprus to a London police station.
 Speaking of foreign: A German production at the Deutsches Theatre in 2001 pushed the boundaries of the character by not only casting a white actor as Othello, but a female one. This more avant-garde production starring actress Susanne Wolff sees Wolff utter her lines in varying costumes progressing from a simple black-and-white shirt and pants ensemble to—believe it or not—a gorilla suit intended to show Othello’s shift from loving partner to a more animalistic creature bent on vengeance. Blogger/reviewer Andrew Haydon says about the production, “Okay, there are two headlines to choose from here: 1) I’ve just seen the best production of Othello I’ve ever seen. 2) I’ve just seen a production of Othello in which Othello is played by a white woman in a gorilla costume. My job, then, is to explain how (2) manages to be (1).”
Speaking of foreign: A German production at the Deutsches Theatre in 2001 pushed the boundaries of the character by not only casting a white actor as Othello, but a female one. This more avant-garde production starring actress Susanne Wolff sees Wolff utter her lines in varying costumes progressing from a simple black-and-white shirt and pants ensemble to—believe it or not—a gorilla suit intended to show Othello’s shift from loving partner to a more animalistic creature bent on vengeance. Blogger/reviewer Andrew Haydon says about the production, “Okay, there are two headlines to choose from here: 1) I’ve just seen the best production of Othello I’ve ever seen. 2) I’ve just seen a production of Othello in which Othello is played by a white woman in a gorilla costume. My job, then, is to explain how (2) manages to be (1).”
Key Scenes in Othello
Consider/review these scenes as you complete your Major Works Data Sheet for Othello and prepare for the seminar:
Act I, Scene 3 – Othello and Desdemona’s stories of their love; The Duke’s and Brabantio’s warnings to Othello; Iago’s advice to Roderigo; Iago’s final speech
Act II, Scene 1 – Iago, Emilia, and Desdemona speaking of men and women; Iago’s speeches regarding his developing plan of revenge
Act II, Scene 3 – Cassio’s downfall and Iago’s advice to Cassio
Act III, Scene 3 – Iago plants and waters the seed of jealousy
Act III, Scene 4 – Othello confronts Desdemona about the handkerchief
Act IV, Scene 1 – Iago “proves” Cassio’s betrayal; Othello and Iago make plans
Act IV, Scene 3 – Desdemona and Emilia talk of men and women
Act V, Scene 1 – Iago puts his final plan into action
Act V, Scene 2 – Othello carries through with his part of the bargain; Iago’s plot is revealed and tragedy befalls the cast
Othello’s Lamentation by William Salter, 1857, from the Folger Library Collection
Comments Off on Key Scenes in Othello
Filed under AP Literature
Tagged as analysis, AP, commentary, discussion, Othello, plays, reading, sources